
what you should know
- status of files, “untracked, unmodified, modified, staged”
- branch include master, brance A, brance B, and so on
help
when you don’t know what to do first, you can use the help command.
git --helpgit sub-command --help, e.g:git commit --help,git checkout --help
config
ssh-keygen -t rsa -C "youremailname@gmail.comgit config --global core.editor "vim"git config --global user.email "abc@gmail.com"git config --global user.name "matrix207"git config --global color.status autogit config --global color.diff autogit config --global color.branch autogit config --global color.branch autogit config --global color.paper "less -r"avoid escape characters ingit log|diffgit mergetool --tool=vimdiff- list configuration:
git config -l - cat ~/.gitconfig
- git auto completion, git-completion.bash
https://github.com/git/git/blob/master/contrib/completion/git-completion.bash
Basic
git clone urlgit pullfetch data and try to merge it the working codegit fetchonly fetch datagit statusgit status -unonot show untracked filesgit diffgit diff --cachedview difference of staged filesgit diff COMMIT_ONE COMMIT_TWO fileview difference for specify file between two commit versiongit diff fa510^ fa510view difference between previous and specify commit version
git rm filesgit rm -r pathremove directorygit add filesgit add .add all files in current directorygit add -u ./only add tracked files to stage
git mv path_fileA path_fileBgit checkout featureAswitch to branch featureAgit checkout a.hrestore file, if you also have a branch named a.h, should use git checkout – a.h”git reset fileunstage file (remove from staged to modified status)git commitcommit message with specify editorgit commit file -m "comment here"git remote -vgit loggit log -p -2difference between the latest 2 updategit log --statshow detail of changed filesgit log --author="dennis"filter log by authorgit log commit_versiongit log -S 'XXX' fileview commit info of specify code of filegit log --no-mergesnot show merge log
git clean -f -nShow what will be deleted with the -n optiongit clean -fremove untracked filesgit clean -fdremove untracked filesgit help cleanfor more informationgit stashadd current modify files to stashgit stash poppop stash filesgit stash listgit stash showgit help stash
Advance
git reset fileundo git addgit checkout HEAD /path/fileundo git operation(rm/modify and so on) on filegit rm $(git ls-files --deleted)undo git rm multiple filesgit reset --hard origin/mastercancel local modifygit reset --soft HEAD~1git help resetgit mergegit merge --squashmerge code without commitgit merge --no-commit
git branchshow all local branch, tell you which is the current branchgit branch -ashow all branch, both local and remotegit branch -vvprint the name of the upstream branchgit branch --contains <commit>find which local branch contain the specify commitgit branch -r --contains <commit>find which remote branch contain the specify commitgit help branchfor more- fork+pull
git commit --amendgit blame fileview all change info of each linegit push origin :branch_namedelete remote branchgit remote update --pruneupdate remote branch information on localgit for-each-ref --format='%(committerdate) %09 %(authorname) %09 %(refname)'\ |sort -k5n -k2M -k3n -k4nlist remote git branches by authorgit status --short |awk '$1 ~/^M|A|U/ {print $2}'only show modified filesvim $(git status --short |awk '$1 ~/^M|A|U/ {print $2}')editor all modified files by vimgit rev-parsegit rev-parse HEADshow commit SHA1 of HEAD
git log -Lshow lines history
other command
- git commit –fix-up
tags
git tag -a v0.1 -m 'new tag version 0.1'add taggit push origin master v0.1push tag to origin
Skills
- reset repository to specify commit version
git clone [remote_address_here] my_repocd my_repogit reset --hard [ENTER HERE THE COMMIT HASH YOU WANT]
- view history version of specify file
git show HEAD:[THE FILE YOU WANT]git show HEAD:[THE FILE YOU WANT] > NEW_NAMEcheckout history commit filegit log FILE_PATH, e.g: git log ./log.cc
- restore file which was deleted at latest commit.
- first, checkout the file
git checkout HEAD^ -- a.txt - second, commit
git add a.txt &&git commit -m "recover a.txt" &&git push
- first, checkout the file
multi line comment for commit
[dennis@localhost git]$ mkdir abc [dennis@localhost git]$ cd abc [dennis@localhost abc]$ git init [dennis@localhost abc]$ echo "123">>1.txt [dennis@localhost abc]$ git commit -m "first commit > > - test log1 > - test log2" [dennis@localhost abc]$ git log commit 98e983f0fdae5ef292083bb5ce288e9344a46751 Author: Dennis <dennis.cpp@gmail.com> Date: Fri Aug 1 09:02:52 2014 +0800 first commit - test log1 - test log2merge commit history
git rebase -i HEAD~2, modify the second ‘pick’ to ‘squash’ to merge the
last two commit into one; If want merge more, just modify 2 to other digit.git push --force origin LOCAL-branch:REMOTE-branch, push to remote repository
modify the latest commit (or using for merge commit history)
git reset --soft HEAD~1, orgit reset --soft <commit id>to edit last
serval commits.- … do something else for the modification …
git commit -c ORIG_HEADto changed the commit message, or usegit commit -C ORIG_HEADto reuse the previous message- reference
git help commit, see the--amend
summary statics
git log --author="$(git config --get user.name)" --pretty=tformat: --numstat \ |awk '{add+=$1;subs+=$2;loc+=$1-$2} END{printf "added lines: %s removed lines \ : %s total lines: %s\n",add,subs,loc}' -count total submit lines of code by authorgit shortlog -s -ncount summary commits by author and sortgit log --pretty='%aN' | sort | uniq -c | sort -k1 -n -r | head -n 5List top 5 commiter
add local repository to remote
git add remote git-urlgit remote -vgit push origin master
Find the modified commit quickly
Assume you find that a function was delete in the current commit, and want to
find which commit changed this.
Normally, you will work as below:
git log FILE-INCLUDE-THE-FUNCTIONto list the commit history of the file
which function belong to.git show COMMIT-SHAand search by the function name
The disadvantage of this method:
- If there lots commit history it would be hard to find.
- It depend the human eyes, ;), which easy to make mistake sometimes.
So, we want a script to execute this task:
- Use
git log --pretty=tformat:%h --after 2015-01-05 FILEfilter by date, and
only show commit hash.git rev-list --all --after 2013-03 FILEwork as well
too. - Use
git show COMMIT-SHA |grep 'KEY-WORDS'to do searching.
With such two skills, we can write bash command as below:git log --pretty=tformat:%h --after 2013-01 FILE |xargs git show |grep -i KEY-WORDS
Conflict handle
- git config –global mergetool=vimdiff
- fugitive
- reference
Other
Auto pull project, bash script
#!/bin/bash
exclude_dir="-I test -I hello"
for i in `ls $exclude_dir`
do
{
if [ -d $i ]; then
(cd $i; echo update `pwd`; git pull)
fi
}
done
gitignore
define ignore files in .gitignore
# ignore all .*.swp files
.*.swp
# ignore all *.out files
*.out
# ignore all *.o files
src/*.o
# files in folder
_site/*
another example:
# Object files
*.o
*.ko
*.obj
*.elf
# Libraries
*.lib
*.a
*.la
*.lo
# Shared objects (inc. Windows DLLs)
*.dll
*.so
*.so.*
*.dylib
# Executables
*.exe
*.out
*.app
*.i*86
*.x86_64
*.hex
again:
_site/*
_theme_packages/*
Thumbs.db
.DS_Store
!.gitkeep
.rbenv-version
.rvmrc
good commit message
Structure your commit message like this:
From: http://git-scm.com/book/ch5-2.html
Short (50 chars or less) summary of changes
More detailed explanatory text, if necessary. Wrap it to about 72
characters or so. In some contexts, the first line is treated as the
subject of an email and the rest of the text as the body. The blank
line separating the summary from the body is critical (unless you omit
the body entirely); tools like rebase can get confused if you run the
two together.
Further paragraphs come after blank lines.
- Bullet points are okay, too
- Typically a hyphen or asterisk is used for the bullet, preceded by a
single space, with blank lines in between, but conventions vary here
- Use a hanging indent
Team work A
- git clone url
- git checkout -b featureA // create a branch, named “featureA”
- coding
- git commit -am “ADD COMMENT HERE”
- git rebase -i // make all commit to be one
- git push origin featureA // push your branch to origin
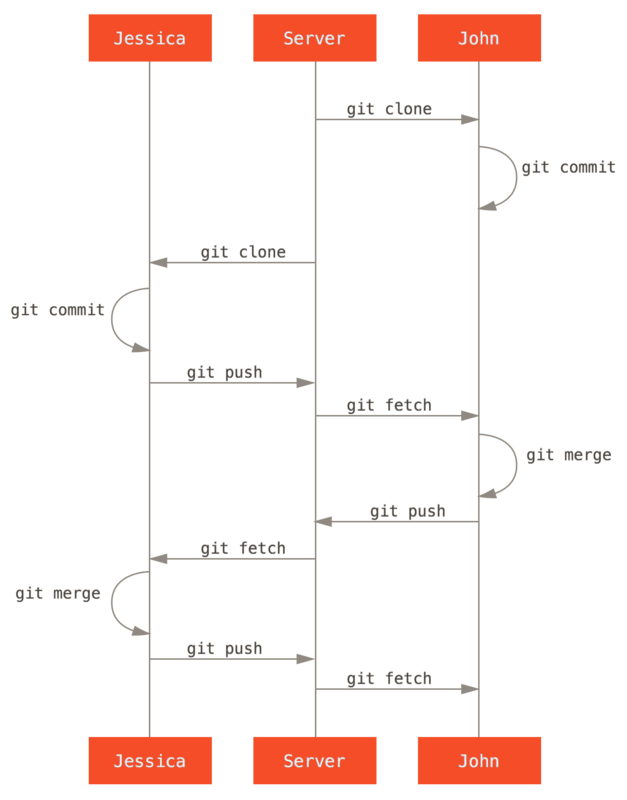
Team work B
- step 1: git check -b branchT1 remotes/origin/branchT1 (you can change your local branch “branchT1” other name if you want)
- step 2: do your coding
- step 3: commit your changeds code to your local branch “branchT1”
- step 4: loop step 2 and step 3
- step 5: git pull origin branchT1 (fetch and merge code, if you not mean do merge, using fetch instead?)
- step 6: git push remotes/origin/branchT1